Galaxy Research, Exploration of large cosmic structures, cosmology

The study of galaxies and even larger structures in the universe is closely linked to cosmological questions, such as how the large-scale structures in our universe came about. This also raises the question of the further development of space. In 2011, three cosmologists were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for their discovery of the accelerating expansion of the universe.
The research community is faced with many more questions. For example, it wants to explore the early universe further or trace down mysterious dark matter.
How are galaxies and large structures researched in Switzerland?
- Observational astronomers characterise the galaxies using spectroscopic and photometric observations. From the results, attempts are made to draw conclusions about star formation history within a galaxy or to understand the formation of various galaxy shapes.
- Other observers are looking for new star systems. There are still many undiscovered galaxies to be found today. Some of these are too faint to be seen in a telescope image. Image processing programs are therefore used to emphasise the inconspicuous galaxies in the image.
- Individual aspects of a galaxy can also be the subject of research. For example, observations are used to investigate how a black hole at the centre of a galaxy influences its development.
- Theoretical groups investigate questions about the structure and development of galaxies with the assistance of numerical simulations on the computer. The result of such a simulation at the University of Zurich is shown in the following film.
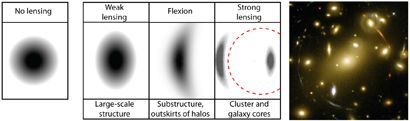
- By observing weak gravitational lenses, researchers gather information about the large cosmic structures. A gravitational lens is a very massive object that lies between us as the observer and another object that we want to observe. Due to its gravity, the massive object bends the rays of light on their way to us. The object we want to observe appears distorted. A weak gravitational lens means that the distortion effect is minor. It is not immediately recognisable to researchers. Only when they observe numerous objects do they use statistical calculations to determine the effect. For visualisation, see also box on right. This provides them with information about the distribution of mass in the universe and dark matter and, consequently, the large structures of the cosmos.