Electromagnetic radiation - wavelength, frequency and energy
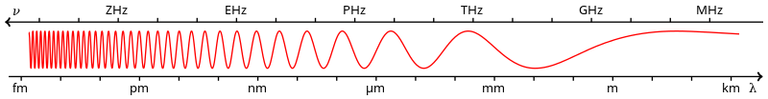
Electromagnetic radiation is a wave that consists of magnetic and electrical fields. Light or microwaves are electromagnetic radiation. It also moves without a carrier medium (i.e. even in space). Sound waves, on the other hand, always require a medium to propagate.
- The wavelength of electromagnetic radiation is the length from one point on the wave to the same point on the next wave. An example is from one wave crest (the highest point of the wave) to the next. The radiation is labelled differently, depending on the wavelength. Examples of very long waves are radio waves, while short waves are gamma rays.
- The frequency of electromagnetic radiation indicates how many wave crests pass through the same location per second. It is therefore the quotient of the speed of light and the wavelength.
- The energy is the product of one of Planck's constant (a natural constant) and the frequency. The energy is usually given in electron volts. This is more suitable than the SI joule unit, as the energies involved are very small.

